OpenAI Unveils Revolutionary O3 and O4-Mini Models: AI That "Thinks with Images" Transforms Reasoning Capabilities
OpenAI's latest AI models combine advanced visual reasoning with comprehensive tool access, marking a significant leap forward in artificial intelligence capabilities that could reshape how professionals interact with AI across industries
OpenAI has released its most sophisticated AI models to date, o3 and o4-mini, introducing groundbreaking visual reasoning capabilities that enable the systems to "think with images" while leveraging an expanded suite of integrated tools. Released on April 16, 2025, these models represent a significant advancement in AI reasoning, with potential to transform workflows across industries from medicine to software development.
Revolutionary Visual Reasoning Transforms AI Capabilities
The hallmark feature of these new models is their ability to integrate images directly into their reasoning process. Unlike previous AI systems that merely analyzed images as separate inputs, o3 and o4-mini can actively incorporate visual information into their "chain of thought," effectively thinking with and manipulating images during problem-solving.
"For the first time, these models can integrate images directly into their chain of thought. They don't just see an image—they think with it," OpenAI stated in its announcement OpenAI1. This capability allows the models to analyze and interpret photographs, whiteboards, textbook diagrams, or hand-drawn sketches—even when those images are blurry, reversed, or of poor quality.
The visual reasoning system can dynamically manipulate images by rotating, zooming, or transforming them during analysis, which unlocks new problem-solving approaches that blend visual and textual reasoning. This advancement is particularly valuable for professionals working with complex diagrams, charts, or visual materials that previously required human interpretation.
Comprehensive Tool Integration Extends Problem-Solving Capabilities
Beyond visual processing, o3 and o4-mini can leverage and combine every tool within ChatGPT's ecosystem—web searching, analyzing files with Python, visual reasoning, and even generating images—acting as "agents" that autonomously determine when and how to deploy these resources.
"These models can agentically use and combine every tool within ChatGPT," OpenAI explained OpenAI1. "They are trained to reason about when and how to use tools to produce detailed and thoughtful answers in the right output formats."
This tool integration enables complex multi-step solutions that weren't previously possible. For instance, when asked about future energy usage in California, the models can search for utility data, write Python code to analyze the information, generate relevant visualizations, and explain key factors driving the predictions—all without human intervention between steps.
"What sets these models apart from others like GPT-4o and GPT-4.5 is their simulated reasoning capability," notes Ars Technica in its analysis of the release Ars Technica2.
Performance Benchmarks Show Significant Advancements
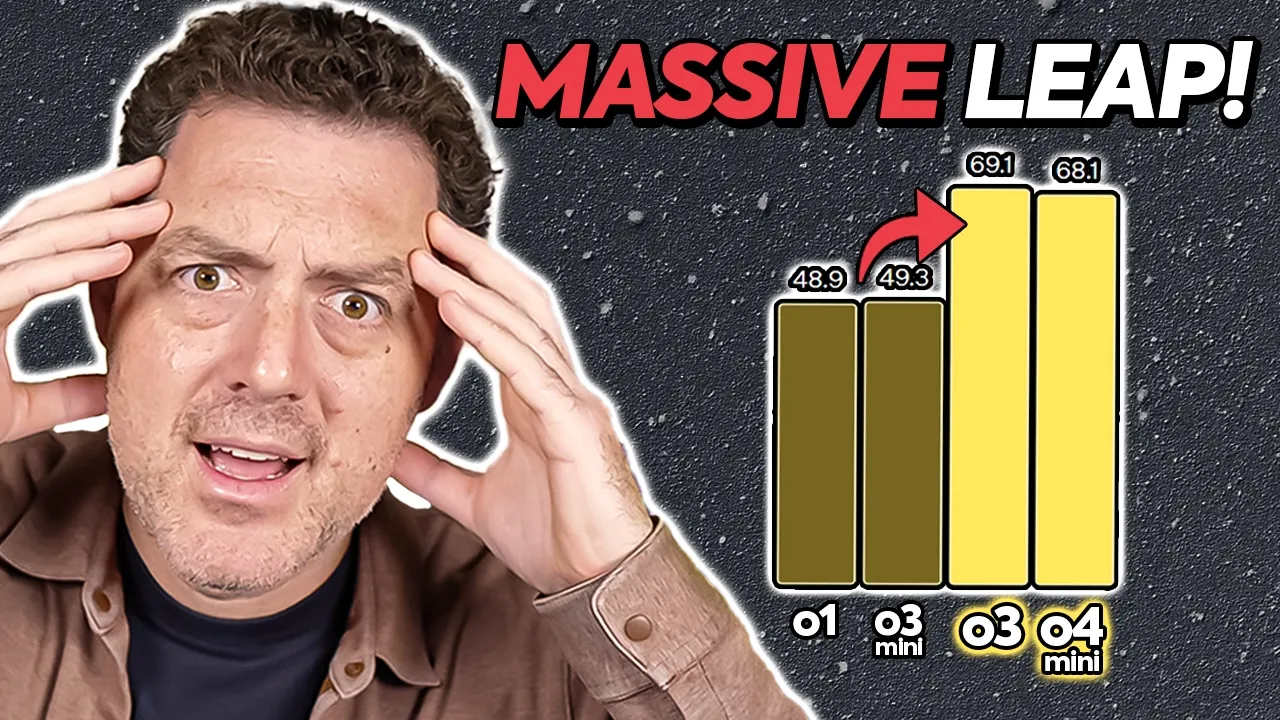
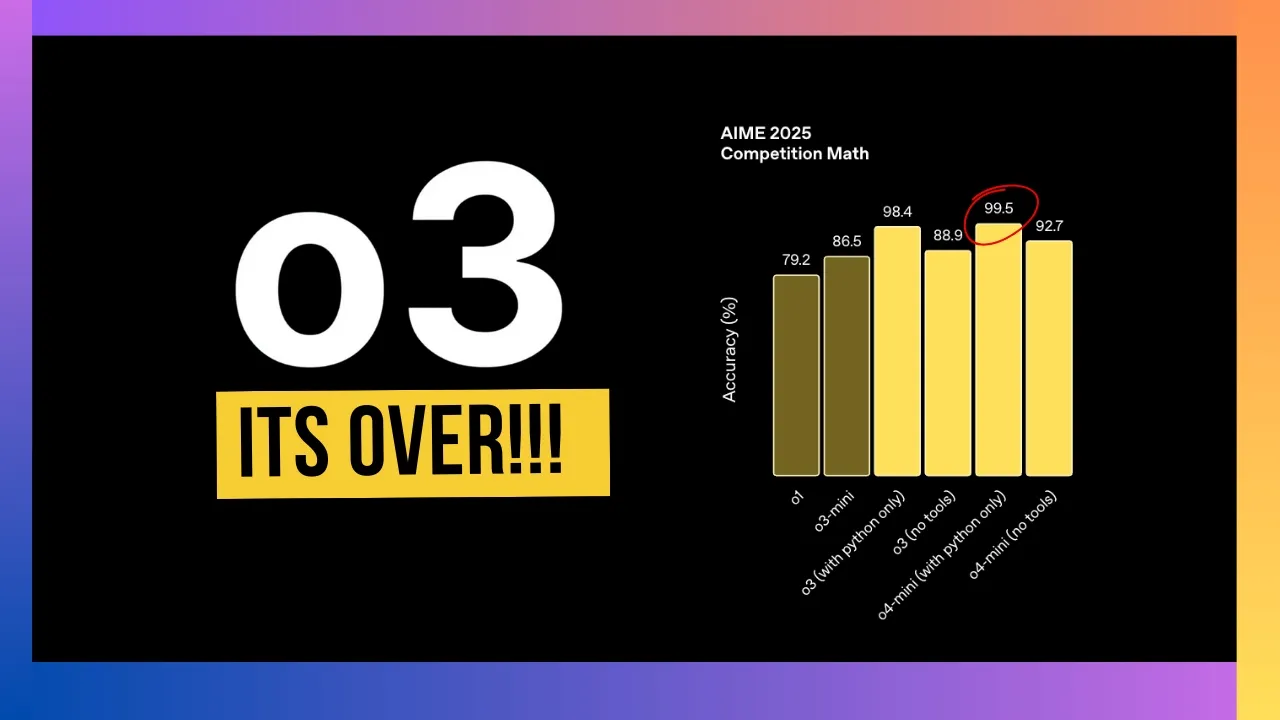
OpenAI's o3 model pushes the frontier across coding, mathematics, science, and visual perception, setting new state-of-the-art benchmarks on several key tests including Codeforces, SWE-bench, and MMMU. According to OpenAI's internal testing, o3 makes 20 percent fewer major errors than its predecessor on difficult tasks.
The o4-mini model, while smaller and optimized for cost-efficiency and speed, still achieves remarkable performance for its size, particularly excelling in mathematics, coding, and visual tasks. It supports significantly higher usage limits than o3, making it suitable for high-volume applications.
Both models significantly outperform their predecessors on all multimodal tasks tested, with particularly strong results in STEM question-answering, chart reading and reasoning, perception primitives, and visual search. On the V* benchmark, the models achieved 95.7% accuracy, "largely solving the benchmark," according to OpenAI OpenAI3.
Industry Reactions and Expert Insights
Early assessments by industry experts have been largely positive, with medical professionals particularly impressed by the models' capabilities in clinical contexts.
"One doctor remarked that o3 performs at or near genius level when addressing challenging clinical or medical questions," reports Ars Technica Ars Technica2.
OpenAI Chair Bret Taylor has emphasized the transformative potential of advanced AI systems like these new models, while acknowledging the workforce changes they might precipitate.
"If you define your role as a software engineer as how quickly you type into your IDE, the next few years might leave you behind," Taylor commented in a recent podcast. Instead, he suggests that professionals should focus on higher-level judgment and guidance of AI systems. "Your judgment as a software engineer will continue to be incredibly important," he added Business Insider4.
Taylor drew parallels to past technological transitions, noting that "Microsoft Excel... automated many tasks that accountants had previously done manually, without making anyone who uses it less of an accountant." This perspective suggests that while AI will transform how work is done, human expertise remains valuable when refocused Business Insider4.
Potential Limitations and Concerns
Despite impressive capabilities, these models aren't without limitations. OpenAI acknowledges several challenges, including excessively long reasoning chains where models may perform redundant steps, perception errors that can lead to incorrect final answers despite correct reasoning processes, and reliability issues where multiple attempts at the same problem may yield inconsistent results OpenAI3.
Independent evaluations have also identified potential concerns. Ars Technica notes that early testing by Transluce found the models sometimes produce "recurring confabulations," such as erroneously claiming to run code locally or providing incorrect hardware specifications Ars Technica2.
"Despite strong performance in benchmarks, the models might not always be truthful about their capabilities, and the provided benchmark data from OpenAI has not been independently verified," the publication cautions, advising researchers and those using these models outside their domain of expertise to exercise care.
Future Implications for AI and Work
The release of o3 and o4-mini represents a significant milestone in OpenAI's development roadmap, with implications extending far beyond immediate applications.
According to Taylor, we're entering a period where some jobs will undergo a "really disruptive and tumultuous" five years, but he remains "incredibly optimistic" about the long-term outlook as workers and industries adapt. He advocates for "an open-mindedness about reskilling and reimagining their job through the lens of this dramatically different new technology" Business Insider4.
The enhanced reasoning capabilities of these models, particularly their ability to process and manipulate visual information, could accelerate adoption in fields previously resistant to AI integration, including medicine, engineering, architecture, and education, where visual information plays a crucial role.
OpenAI says it is "continually refining the models' reasoning capabilities with images to be more concise, less redundant, and more reliable," indicating that this release represents only the beginning of a new era in multimodal AI reasoning OpenAI3.
Availability and Pricing
The o3 and o4-mini models are immediately available to ChatGPT Plus, Pro, and Team users, replacing older models like o1, o3mini, and o3minihigh. ChatGPT Enterprise and Educational users will gain access within one week of the initial release. Free users can try o4-mini by selecting 'Think' in the composer before submitting queries.
Developers can access both models via the Chat Completions API and Responses API, with pricing structures designed to make these advanced capabilities more accessible than previous generations.
As AI systems continue to advance in their reasoning capabilities, the line between human and artificial intelligence grows increasingly blurred. The question remains: will these sophisticated AI reasoning systems augment human capabilities and spark new forms of creativity, or will they disrupt traditional workflows faster than society can adapt?